Cloud vs. On-Premise Load Testing: An ROI Comparison
In today’s fast-paced business world, user experience is everything. As companies work hard to stay ahead of the competition and keep up with customer demands, their services are becoming more complex. This growing complexity, combined with the pressure to roll out new features and updates quickly, can sometimes lead businesses to overlook a crucial aspect: ensuring their applications can handle both current and future growth without slowing down.
In the rush to launch new products, some companies may not dedicate enough time or resources to thoroughly test and optimize their systems. As a result, their applications can struggle to deliver fast response times, especially when faced with high user volumes or unexpected traffic spikes.
Thankfully, some IT leaders have learned from past challenges and successfully incorporated performance engineering into their DevOps processes. They start early with performance analysis during the design and development stages, automate tasks, review results, and tackle bottlenecks before they become problems. Load testing has become a key part of performance testing, helping to simulate real-world scenarios and assess how a system performs under different levels of stress and load. Choosing the right load testing tools, though, involves considering several factors, including cost and return on investment (ROI). In this article, we’ll compare the ROI of cloud-based vs. on-premise load testing tools, taking a closer look at their costs, savings, and other important factors.
Costs of Performance Testing: On-Prem vs. Cloud
Creating responsive applications that remain strong and maintain acceptable response times during periods of increased load isn’t a straightforward task. It’s not as simple as buying a performance solution off the shelf and instantly resolving all performance bottlenecks. The truth is there’s no one-size-fits-all remedy for poor performance. Organizations need to invest in skilled engineers, acquire appropriate tools, and establish performance testing frameworks within their infrastructure to consistently tackle performance challenges.
When it comes to performance testing, it typically incurs several different costs such as costs primarily revolving around tooling, infrastructure, and personnel. When opting for on-premise load testing tools, organizations need to invest in procuring hardware, software licenses, and maintaining infrastructure. These upfront costs can be substantial, especially for large-scale testing requirements. Additionally, ongoing expenses such as maintenance, upgrades, and personnel training contribute to the total cost of ownership (TCO) for on-premise solutions.
On the other hand, cloud-based load testing tools present a distinct advantage in terms of cost structure. Rather than committing to upfront investments in hardware and software licenses, users can opt for usage-based pricing models. These models often operate on a per-test basis or through subscription plans. While this pay-as-you-go model may appear cost-effective at the outset, it’s crucial to note that expenses can increase over time, especially for organizations conducting extensive testing or experiencing sudden spikes in demand.
Savings of Performance Testing: Cloud Compared to On-Prem
Despite the costs involved, performance testing can yield significant savings by identifying and mitigating potential issues early in the development lifecycle. By uncovering performance bottlenecks and vulnerabilities, organizations can avoid costly downtime, reputation damage, and lost revenue resulting from poor user experiences. It’s difficult to calculate and measure the true financial impact of this but as we know in today’s day and age, your customers and users are crucial to ensuring that your business is doing well. Between the reputational gains and increased trust from your users, you’re providing them with an unforgettable experience and if you fail to deliver on that, your own users will turn against you. Overall, your ability to proactively address performance issues before deployment can lead to substantial savings in terms of remediation efforts and customer retention.
Additional benefits include increases in revenue and earnings due to performance problems detected ahead of time. Amazon, for instance, has demonstrated that a 100ms speed improvement increased their sales by 1 percent. When users experience slow loading web pages, they often abandon and spend their money on a competitor’s website. Load and performance tests help companies fix such slowdowns early in the lifecycle, protecting their online revenue streams. Those fixes in the pre-production stages are easier to implement and result in additional savings for the organization.
When you’re looking for a load testing tool, note that cloud-based load testing tools offer additional savings through their scalability and flexibility. With the ability to scale resources dynamically based on your testing requirements. Your organizations can optimize costs by only paying for the resources they consume. Moreover, cloud platforms often provide built-in monitoring and analytics capabilities, empowering your teams to gain insights into application performance without investing in additional tools or infrastructure. And this leads to the next point. Typically, cloud-based solutions help to alleviate the burden of maintaining and upgrading hardware, software, and infrastructure that you would find in an on-premise load testing tool. This helps to reduce the total cost of ownership in the long run. By leveraging the expertise of cloud load testing tools, organizations can streamline operations, enhance agility, and focus on core business activities, thereby maximizing ROI from their performance testing initiatives.
Calculating ROI Performance
Have you ever considered evaluating the tangible expenses and benefits of your load and performance testing services?
Let’s dive into a comparison between an on-premise setup and a cloud (SaaS) load testing solution to illustrate this.
Take note of the following key figures that you might need to consider in your ROI in this example:
- 1,000 concurrent user load testing tool licenses
- 120 test executions per year
- 800 HTTP based and 200 real browser-based users in each test run
- 58 load injection machines
- $6,000 annual costs for each load injection server
- 120 performance defects per year
- 20% fewer defects on production due to load testing
- 2 performance engineers earning $60,000 annually
Not considered in this calculation/consideration are:
- Increases in sales due to less abandon rates
- Efforts to fix identified performance defects
- Additional compensation benefits and incurred costs of the two performance engineers
ROI for On-Premise Load Testing Platforms
Companies deploy on-premise load testing suites on dedicated servers hosted in their datacenters. There are some open-source solutions with limited user simulation features on the market, but professional businesses typically rely on commercial platforms. The vendor of this load testing suite charges an initial license fee of $300,000 and an annual maintenance fee of $60,000.
Two engineers are responsible for load and performance testing in this company, and they identify 120 performance defects per year. The company is using 58 dedicated load injection machines which result in additional expenses of $6,000 annually per machine. On the savings side, there are 20 percent fewer defects in production. Further aspects, such as the impact on revenue or less rework activities, will not be considered in this scenario for the sake of simplicity.
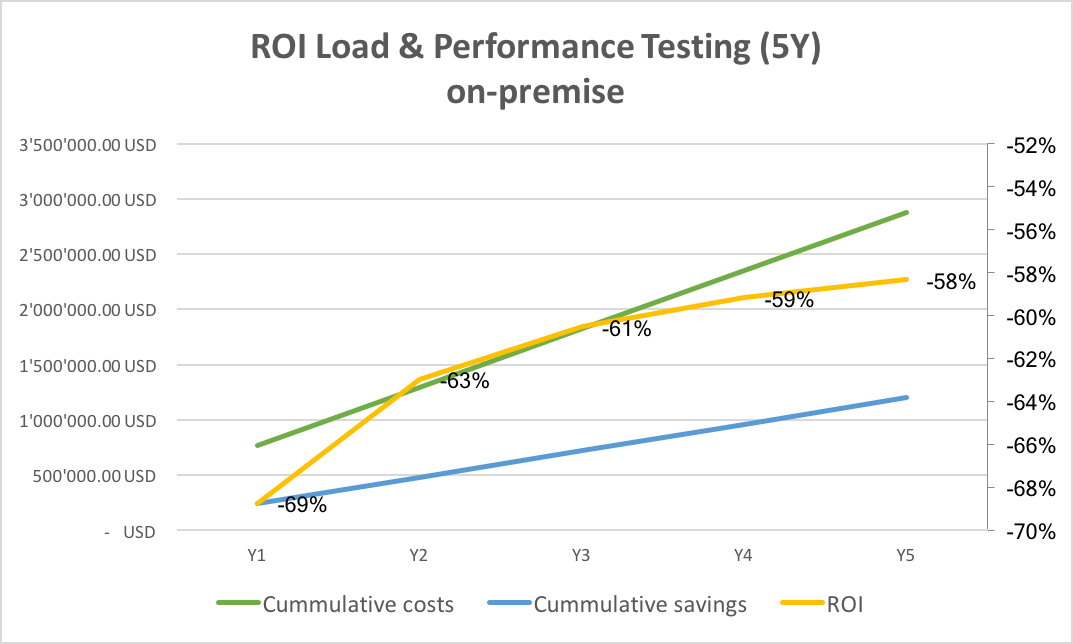
The chart below shows how expenditures, earnings, and the corresponding ROI progress over five years. This calculation shows that an organization that relies on an on-premise load and performance-testing platform realizes a negative -58% return on their load and performance testing investments after five years.
ROI for Cloud Load Testing Platforms
SaaS-based load and performance testing suites operate entirely in the cloud. The provider manages the load agent machines and handles the operation and maintenance of both the load testing software and the underlying infrastructure. Organizations are only charged for permanent storage of their test results and the actual utilization of virtual user minutes. Thanks to the streamlined maintenance requirements of a SaaS-based solution, the organization can reduce the size of its load and performance testing team to just four members.
On the savings side, there are 20 percent fewer defects in production. Further aspects, such as the impact on revenue, will not be considered in this example for the sake of simplicity.
The chart below stresses the costs, savings, and ROI of an on-demand cloud-based load and performance testing platform over five years. This calculation shows that organizations that rely on SaaS-based load and performance testing platforms realize a 12 percent return on performance testing investments.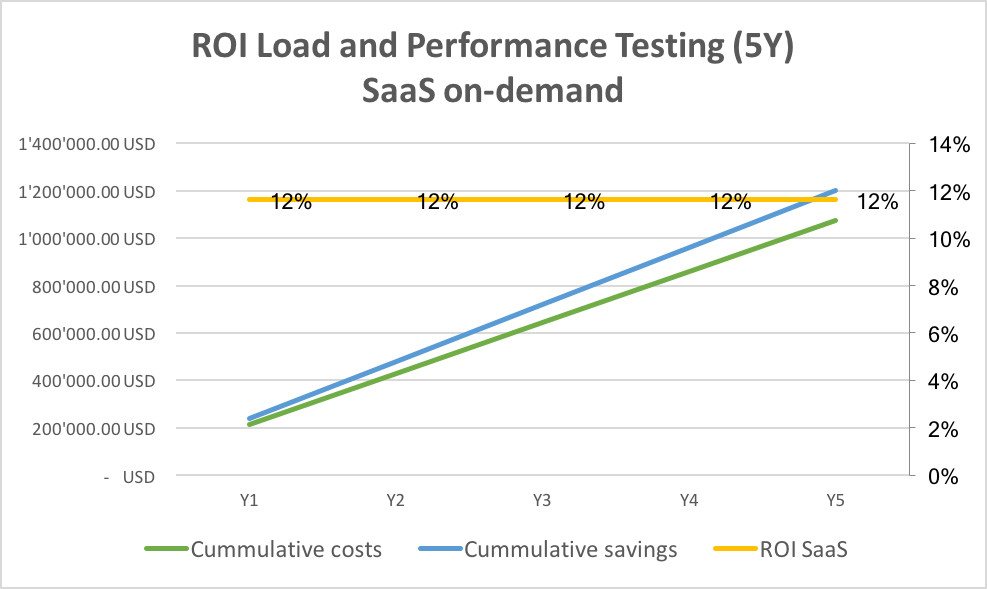
Comparison Between On-Premise and Cloud Load Testing Tools
What factors affect return on investment (ROI), and when does an on-premise load testing suite become more cost-effective than a cloud-based platform?
Cloud-based load testing solutions typically incur charges based on virtual user minutes. The frequency of test executions significantly influences the ROI of cloud-based solutions. Conversely, on-premise load and performance testing suites deployed locally don’t face this cost factor, as they operate on a static license fee that remains consistent regardless of the number of tests conducted.
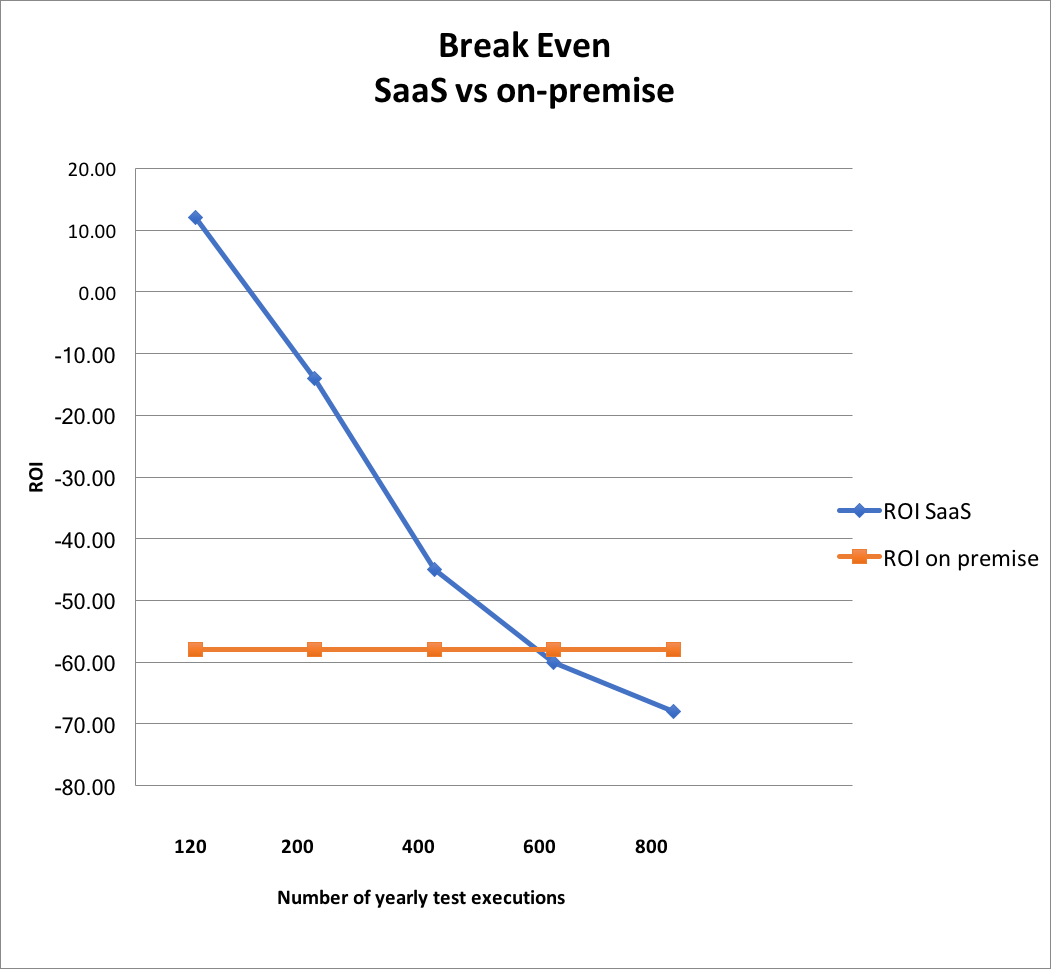
At 120 test executions per year, cloud-based solutions deliver an ROI of 12 percent, while on-premise platforms fall behind with a -58 percent ROI. If this company decides to execute 600 load tests annually, cloud-based load and performance testing platforms will reach an equivalent ROI to that of on-premise solutions. Increasing beyond 600 load test executions will see on-premise platforms yielding higher ROI than full cloud-based platforms.
The chart below illustrates the progression of ROI on performance investments over a five-year period for companies conducting between 120 to 600 load tests annually.
Conclusion: What Else to Consider
When evaluating the ROI of load testing tools, organizations must consider factors beyond costs and savings. Key considerations include:
- Scalability: Cloud-based solutions offer inherent scalability, allowing organizations to accommodate fluctuating testing demands seamlessly. In contrast, scaling on-premise infrastructure may require significant investments and lead times.
- Security and Compliance: Organizations must assess the security posture and compliance requirements of both cloud-based and on-premise solutions. While cloud providers adhere to strict security standards, some industries or regulatory frameworks may require on-premise deployments for compliance reasons.
- Integration and Compatibility: Compatibility with existing tools, platforms, and workflows is crucial for seamless integration and collaboration across your teams. Your organization should evaluate the load testing tools with their existing infrastructure and development stack in mind. You want to ensure that it’s easy to implement, get up and running, and work with your teams.
In conclusion, the choice between cloud-based and on-premise load testing tools involves a careful analysis of costs, savings, scalability, security, and compatibility. While on-premise solutions offer control and customization, cloud-based offerings provide scalability, flexibility, and potential cost savings. Investing in cloud-based load and performance testing suites outperforms on-premise platforms in most scenarios. The ROI of cloud-based load testing platforms is already positive in the first year, while on-premise solutions deliver a negative ROI during the five-year test period. One main reason for better ROI of cloud-based solutions is that there are no licensing costs, no maintenance efforts, and no internal infrastructures involved.
If your team is looking for a cloud-based load testing tool that offers flexibility, scalability and is rich with load testing features, consider LoadView. LoadView offers a user-friendly platform for your load testing efforts that can easily integrate with your favorite tools that you’re already using in your technology stack. The in-depth reporting and analysis that you get from LoadView provides your teams with a powerful advantage in being able to identify and resolve potential bottlenecks early on in your development stages.
Ultimately, organizations must align their choice of load testing tools with their specific requirements, objectives, and budgetary constraints to maximize ROI and ensure optimal performance of their applications in production environments.