GraphQL is a query language for API and a server-side runtime for inquiries by checking a sort framework for your information. GraphQL isn’t attached to a particular information base or capacity motor and is upheld by your current code and data. A GraphQL administration is made by characterizing types and fields on those sorts, at that point giving capacities to each lot on each kind. For instance, a GraphQL administration that reveals to us whom the client signed is (me) just as that client’s name may look like this:

Why and Where GraphQL is Used?
With GraphQL, the user can settle on a solitary decision to bring the necessary data instead of building a few REST solicitations to obtain the equivalent. The choice to accurately create the client’s data is a uniquely favorable position over sending different REST calls to get the equivalent. To produce the data utilizing REST calls would require a two-phase measure — One to accumulate the client’s data and bring the data about the association the client is related. GraphQL mitigates this two-advance cycle.
If you have stable relaxing assistance, there’s most likely not a solid case to throw the entirety of that work out. Any of these examples could be actualized with an alternate device. I’d contend utilizing GraphQL would bode well in actualizing these examples because the solicitation/control of information (inquiry) is decoupled from the execution of those activities.
How GraphQL Differs from REST and SOAP
While REST was a sort of an innovative achievement in the zone of API-arranged design, it, despite everything, left engineers needing more. When Facebook folks began searching for an alternate method of bringing information from the worker, they attempted to determine the under-getting or over-getting issue that the current API conventions had. In REST or SOAP, a solicitation for certain information restored all properties related to it; even those the client didn’t require.
GraphQL was intended to deal with this issue. At the point when you make an information request, you determine what you wish to get. Such outcomes are accomplished through moving the information definition capacities to the customer side, while in REST, information is characterized on the worker side. As such, in REST API design, the worker represents which data is to be returned, while in GraphQL API, the worker proclaims the accessible information, and the customer indicates what ought to be replaced.
Advantages of GraphQL
- Fit for complex systems and microservices
- It is fetching data with a single API call
- Tailoring requests to your needs
- Validation and type checking out-of-the-box
- Autogenerate API documentation
- API evolution without versioning
- Code-sharing
GraphQL Disadvantages
One drawback is that questions consistently return an HTTP status code of 200, whether excessively inquiry was effective. Another drawback is the absence of implicit storing support. Since REST APIs have various endpoints, they can use local HTTP storing to abstain from pre-fetching assets.
Native Tools to Enhance GraphQL-based API Performance
GraphiQL
A lot of GraphQL APIs utilize the GraphiQL open-source tool as an intelligent API play area. GraphiQL is the IDE (Integrated Development Environment) for communicating with GraphQL API calls, empowering designers to question information, and perform transformations. The IDE is generally simple to actualize. For Node JS developers, express-GraphQL can consequently create GraphiQL. Since it’s based on React, GraphiQL can likewise be infused with one of a kind CSS for custom marking.
GraphQL Voyager
In case you’re planning to outwardly perceive how social your information is, sending it into Voyager can make for fun analysis. Explorer takes a GraphQL API and transforms it into a chart. After setting a root construction, you can see how fields and types are associated. Explorer is intelligent, as well — choosing a sort of features the areas it is contained, and connections to important information inside the diagram.
Voyager gives a left section that portrays field data and a visual interface that users can move through. Clients can likewise streamline the diagram by dispensing with Relay covering classes. Past being a cool way to visualize your data, the Voyager instrument could assist organizations with imagining their information model and sparkle discussions on social information. At last, we can see the “chart” behind GraphQL.
GraphCMS
GraphCMS is an API-driven Content Management System (CMS) that is personally attached to GraphQL, allowing users to construct a facilitated GraphQL for web applications, giving tooling to oversee content. Clients characterize information structures, approve them in GraphQL support, and see the UI’s portrayal, all inside a similar stage.
GraphCMS may not be a solid match for a current API platform, it would be a good fit for a blog, application, or other applications that require the capacity to share information automatically. A CMS based on GraphQL would be a fascinating option in contrast to other popular CMS platforms, such as WordPress or Drupal, and would empower a more adaptable solution that is API-ready for user interfaces.
GraphQL Faker
If you’re modeling a basci API, adding some test text for testing can help. Engineers can embed practical information to copy genuine outcomes with Faker. It’s controlled by Faker.js, empowering engineers to taunt more than 60 sorts of useful information, similar to addresses, first names and last names, symbol pictures, and that’s just the beginning. Everything you require to start is composing a GraphQL Interface Definition Language (IDL), and Faker gives a few guides to begin inside the IDL proofreader. It’s as easy as adding an order to a field:
type Person {
name: String @fake(type: firstName)
gender: String @examples(values: [“male”, “female”])
}
Load Test a GraphQL-based API with LoadView
LoadView supports a Postman API client feature, allowing users to send REST, SOAP, WSDL, and GraphQL requests.
Step 1: We will export collection. Then import to LoadView.
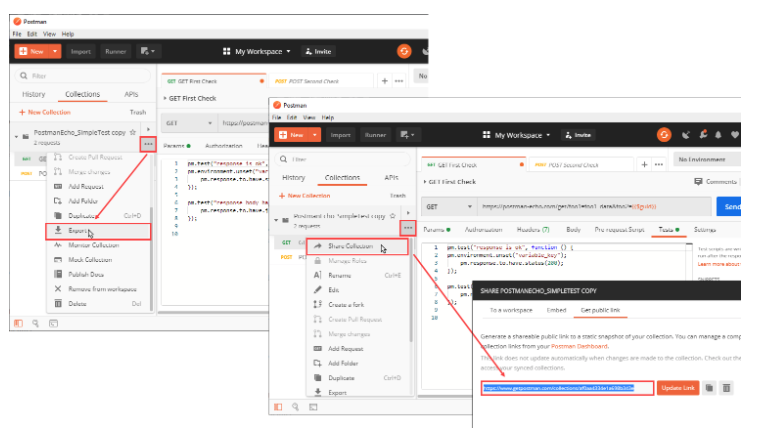
Step 2. Log in to LoadView and select Postman Collection
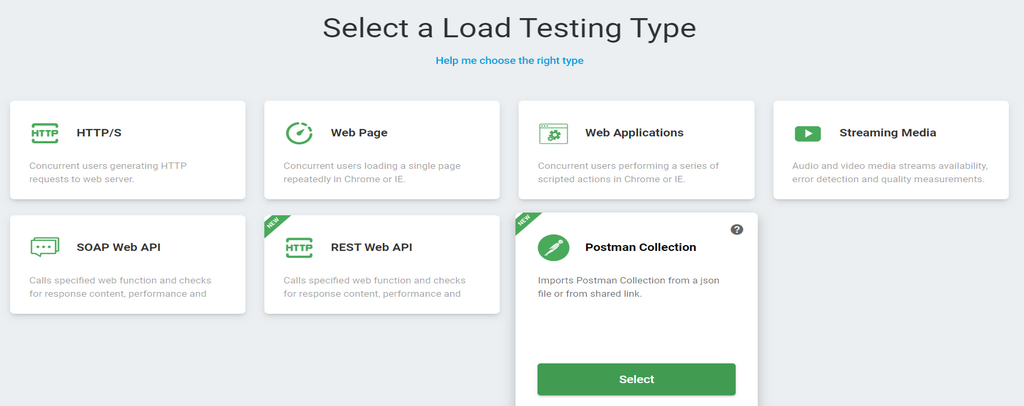
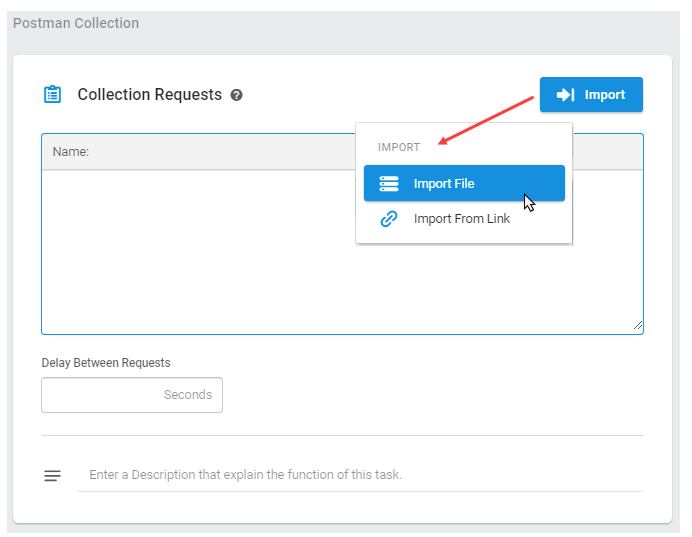
Step 3. Import your Postman collection and select Create Device.
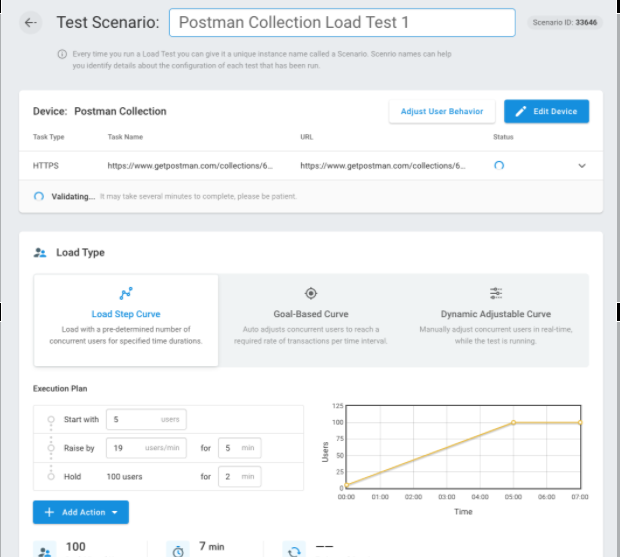
Step 4: After creating your device, you will need to set up your test scenario. Choose from multiple load test types – Load Step Curve, Goal-based Curve, and Dynamic Adjustable Curve. Additionally, you can set the locations for your load injectors. Choose from more than 15 locations from around the world.
After your test is complete, you can view various performance data and charts, including average response times, errors, element-level metrics, and more.
Wrap Up: Load Testing GraphQL Web APIs
There are a lot more GraphQL APIs that appear to be rising every day. Ideally, with the approach of tools like the ones referenced in this article, more companies can realized the benefits of GraphQL APIs and load testing APIs with LoadView is simple and easy.
Start automating your API performance tests with LoadView by signing up for the free trial today.
GraphQL logo: Facebook / BSD (http://opensource.org/licenses/bsd-license.php)